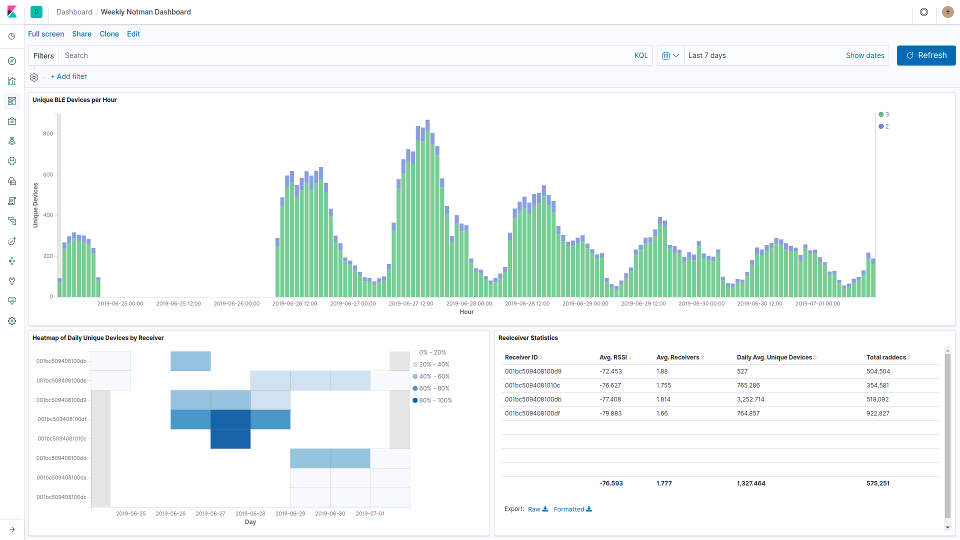
Flight Plan: BLE RTLS
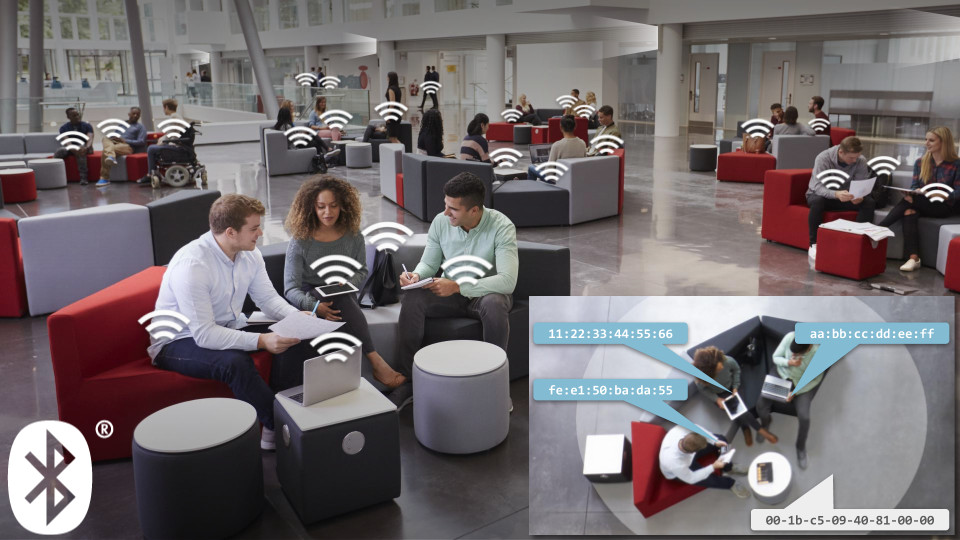
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a low-power, wireless, personal area network technology. Since 2014, over 1 billion BLE devices have shipped annually. These include smartphones and wearables likely to be carried by people, as well as inexpensive beacons and sensors likely to be affixed to assets or physical places. One key feature of BLE is its support for spontaneous advertising packets: any BLE device can announce itself to any listening device in range (typically 10m+), including identifiers and sensor data in the payload.
Real Time Location Systems (RTLS) estimate the location of people and assets within physical spaces, in (or near) real-time. In most cases, infrastructure within the space will detect and identify people and assets via radio-frequency devices that they carry. The location of these devices can be coarsely estimated by standard means such as signal strength, and/or finely estimated by specialized means such as Angle of Arrival, Time Difference of Arrival, etc., when supported by the devices and infrastructure.
BLE RTLS is a promising technology due to the relative ubiquity of both devices and infrastructure. Chances are you yourself carry at least one BLE device (smartphone, wearable, key tracker, etc.) and that there is at least one fixed, powered BLE device (SmartTV, set-top-box, access point) within about 10m. As a result, it would be possible to observe anonymous occupancy patterns in many spaces today. And, with the necessary opt-in from device users and infrastructure owners, ubiquitous real-time location becomes a real possibility.