What is RPKI?
RPKI stands for Resource Public Key Infrastructure. RPKI proves the association between specific IP address blocks or Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) and the holders of those Internet number resources.
RPKI stands for Resource Public Key Infrastructure. RPKI proves the association between specific IP address blocks or Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) and the holders of those Internet number resources.
ARIN is the American Registry for Internet Numbers – the organization responsible for the management and distribution of Internet number resources such as Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) in several regions, including Canada.
Hosted Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) is an infrastructure in which ARIN hosts a Certificate Authority (CA) and signs all Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) for resources within the ARIN region.
An RSA is an agreement between your organization and ARIN regarding your IP address space and any ASNs you have. The RSA has undergone multiple version updates to enhance the power of the resource holder and to make use of Hosted RPKI.
An LRSA is a legacy agreement between your organization and ARIN regarding your IP address space and any ASNs you have. The current RSA Version 13.0 and LRSA Version 5.0 are a unified and single document. The RSA/LRSA has undergone multiple version updates to enhance the power of the resource holder and to make use of Hosted RPKI.
A legacy number resource is an IPv4 address or Autonomous System Number (ASN) that was originally issued to the current registrant by an Internet Registry (InterNIC or its predecessors) prior to the inception of ARIN on December 22, 1997.
Yes. Any new legacy resources brought under an LRSA as of January 1, 2024 onwards will fall under the standard Registration Services Plan fees. The opportunity to take advantage of the Legacy Fee Cap will expire January 1, 2024. All organizations with active LRSAs entered prior to January 1, 2024, will continue to have their fees limited. Any new legacy resources brought under an LRSA after January 1, 2024 will fall under the standard Registration Services Plan fees.
Yes. The standard ARIN RSA can be found here for review by an organization or their legal department. This agreement was released September 12, 2022, and is a combined RSA version 13.0/LRSA version 5.0.
Yes. The standard ARIN RSA can be found here for review by an organization or their legal department. This agreement was released September 12, 2022, and is a combined RSA version 13.0/LRSA version 5.0.
Inform ARIN that you are looking to participate in RPKI as you create your RSA. You may contact the Registration Services Help Desk at 1-703-227-0660 or by submitting an “Ask ARIN” ticket via your ARIN Online account to initiate creation of a RSA/LRSA.
A Route Origin Authorization (ROA) is a key component of RPKI where the legitimate IP resource holder makes a certifiable statement about which network Autonomous System (AS) should originate an IP prefix(es). ROAs may only be generated for Internet Number Resources listed on your resource certificate.
ROV is a security mechanism that allows you to verify the authenticity and accuracy of BGP announcements. ROV relies on data in RPKI.
An RPKI Resource Certificate identifies the IP resources that can be used when creating a ROA.
There is no ARIN policy that requires the use of RPKI. RPKI is an opt-in feature with ARIN. However, a growing number of service providers require you to make Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) for your resources before finalizing a business agreement (e.g., TELCO Systems, BYOIP).
At ARIN, RPKI Resource Certificates are set with a two-year lifespan, and they auto-renew after one year, resetting the two-year lifespan.
RPKI ROAs are created with a 90-day lifespan. They auto-renew after 80 days, resetting the 90-day lifespan.
Given the number of different routing platforms that could be used, we recommend looking at the vendor documentation for the equipment you have installed in your network for RPKI-specific configuration instructions.
No, ARIN’s Whois does not show if statements have been made about IP resources in RPKI. Aside from running an RPKI validator, free third-party tools are available online that show the state of routing announcements or whether ROAs have been created for prefixes.
Given the number of different routing platforms that could be used, we recommend looking at the vendor documentation for the equipment you have installed in your network for RPKI-specific configuration instructions.
Only network operators that perform, or plan to perform Route Origin Validation (ROV) need RPKI-specific configurations to be applied to their routers. These operators typically provide transit for their downstream customers and announce routes to multiple other transit provider networks. If your network does provide route advertisements on behalf of other organizations, you do not need RPKI-specific configurations on your routers.
If your organization doesn’t have a public ASN assigned, your routing announcements are being handled by your upstream provider (your NREN Partner, for example). You can sign up for Hosted RPKI services and create ROAs for your IP resources using your provider’s ASN as the Origin AS.
First, you must ascertain whether you own your IP space:
If YES, you will need to confirm direct allocation on the ARIN website.
If NO, check with your provider and confirm how they are addressing RPKI.
NOTE: If you do not own your ASN, work with your NREN Partner to determine the solution.
The application process for LRSA can be found here.
“Directly Allocated” refers to IP resources that ARIN has assigned specifically to your organization. On the other hand, “Reassigned or Reallocated” denotes IP resources you have obtained from an ISP.
To confirm if your IP resources are a direct allocation, log in to your ARIN Online account.
If any of your networks are not covered by an agreement, they will be highlighted in yellow.
OR
There are two reasons to get your RSA signed as soon as possible:
For any questions regarding your account, contact ARIN here.
You will need to ensure your registration is up to date.
OR
Please note this could negatively affect your production network. Proceed with caution, and if you are not sure what to do, reach out to your NREN Partner for guidance. Visit ARIN’s website and follow the steps outlined here.
Create an ROA matching each route you are advertising.
It can take up to an hour for the ROA to be created.
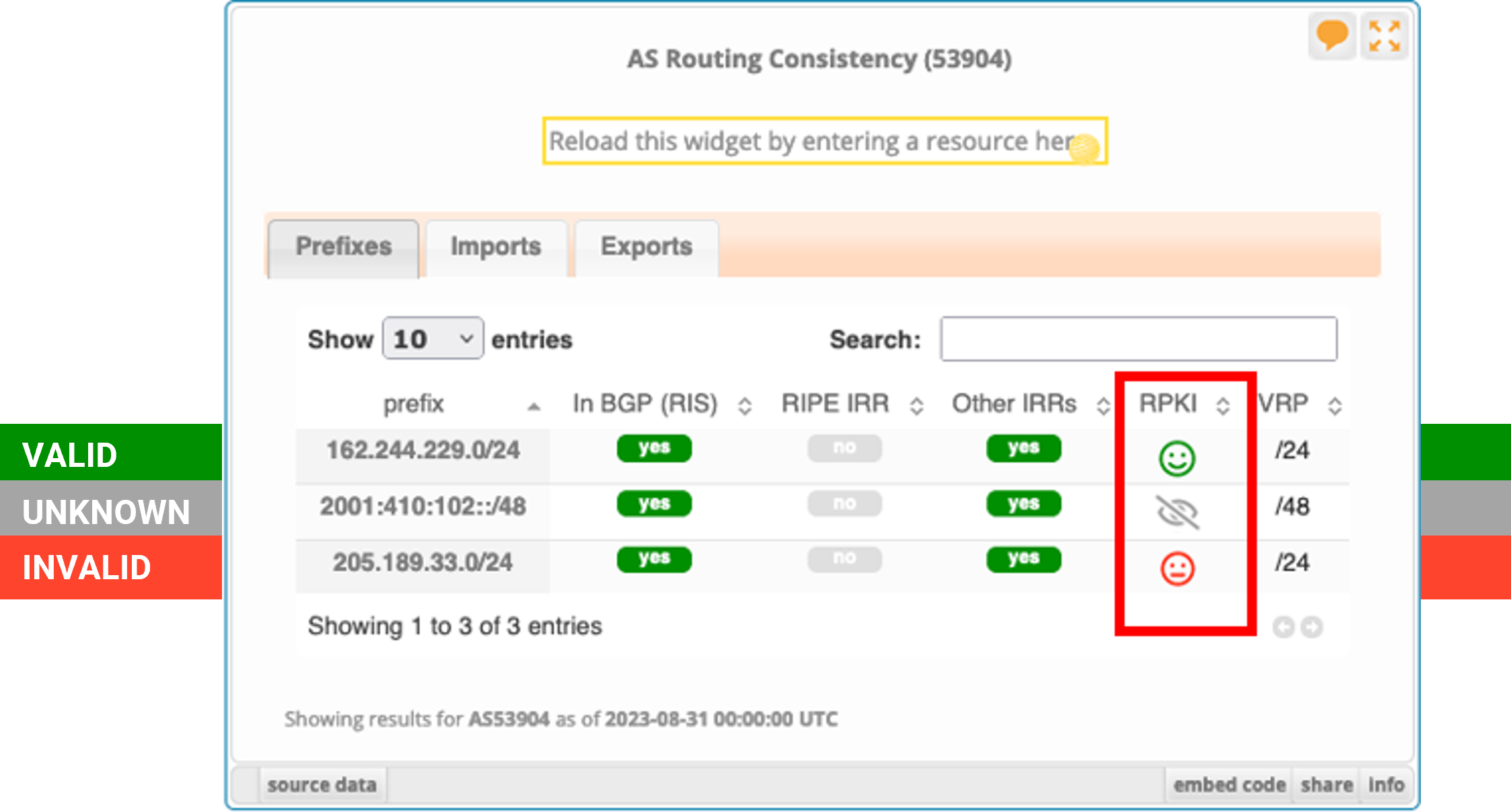
You can use either a public Looking Glass tool or one provided by your NREN Partner to confirm your status. The results of the tool will indicate your RPKI status as either Valid, Invalid, and Unknown as shown here:
ARIN’s Trust Anchor Locator (TAL) is a file that contains both the location of ARIN’s Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) repository and ARIN’s public key, which is used to cryptographically verify that ARIN has signed the artifacts within ARIN’s RPKI repository. The TAL is used with an RPKI Validator to verify the certificates and ROAs within ARIN’s RPKI repository. This validated information can then be used to make routing decisions in your network.
No, TALs are used by ARIN, not individual organizations.
Your regional NREN Partner will be able to provide guidance on these topics.